Multi-Tasking Portfolio

|
Author: Chris Miceli |

|
Dated: 2019-01-03 |

|
Uploaded: 2019-01-03 |

|
Last Edited: 6 years ago |
Abstract
This document defines, documents and lists five threaded java programs which demonstrate a range of concurrency concepts. These programs cover both shared & distributed memory models, providing protocols allowing processes to access and share data between both threaded objects and across multiple clients respectively.
Introduction
This portfolio includes a collection of five fully documented, commented and functional java programs based on provided scenarios. These programs include a car park queue manager, the classic dining philosophers problem, a supermarket checkout simulations represented through a graphical user interface, a chatroom application and a text based server-client game. These are implemented in a multi-threaded java environment, and cover both shared and distributed memory models. Deadlock, liveness, starvation and memory consistency are avoided by ensuring synchronisation, implementing locks and wait notify features into program logic.
Car Park
Problem Definition
This simulation defines a car park containing a fixed number of spaces, accepting and releasing cars from appropriate queues without exceeding capacity. Cars arrive and leave, parking for a random period of time. The queue of cars is overseen by a manager, who is repressible for regulating the flow of incoming and outgoing cars, whilst ensuring capacity is not exceeded.
Solution
The car park contains two queues, one for arrivals and the other for departing cars, each represented by an array list. The manager thread alternates attention between IN and OUT queues, processing cars at a fixed rate on a first come first serve basis. This ensures when both queues are occupied, equal attention is given to both, and when only one queue contains cars, attention is fully devoted to clearing that queue. Each arriving car is first added to an IN queue, eventually processed by the manager and, subject to space availability, assigned to a unique parking thread. Remaining spaces are calculated by de/incrementing an integer when cars arrive and leave the parking lot. The thread contains a sleep timer, representing the amount of parking time a car has remaining.Upon expiration, the car assigns itself to the OUT queue. Image A depicts the described approach.
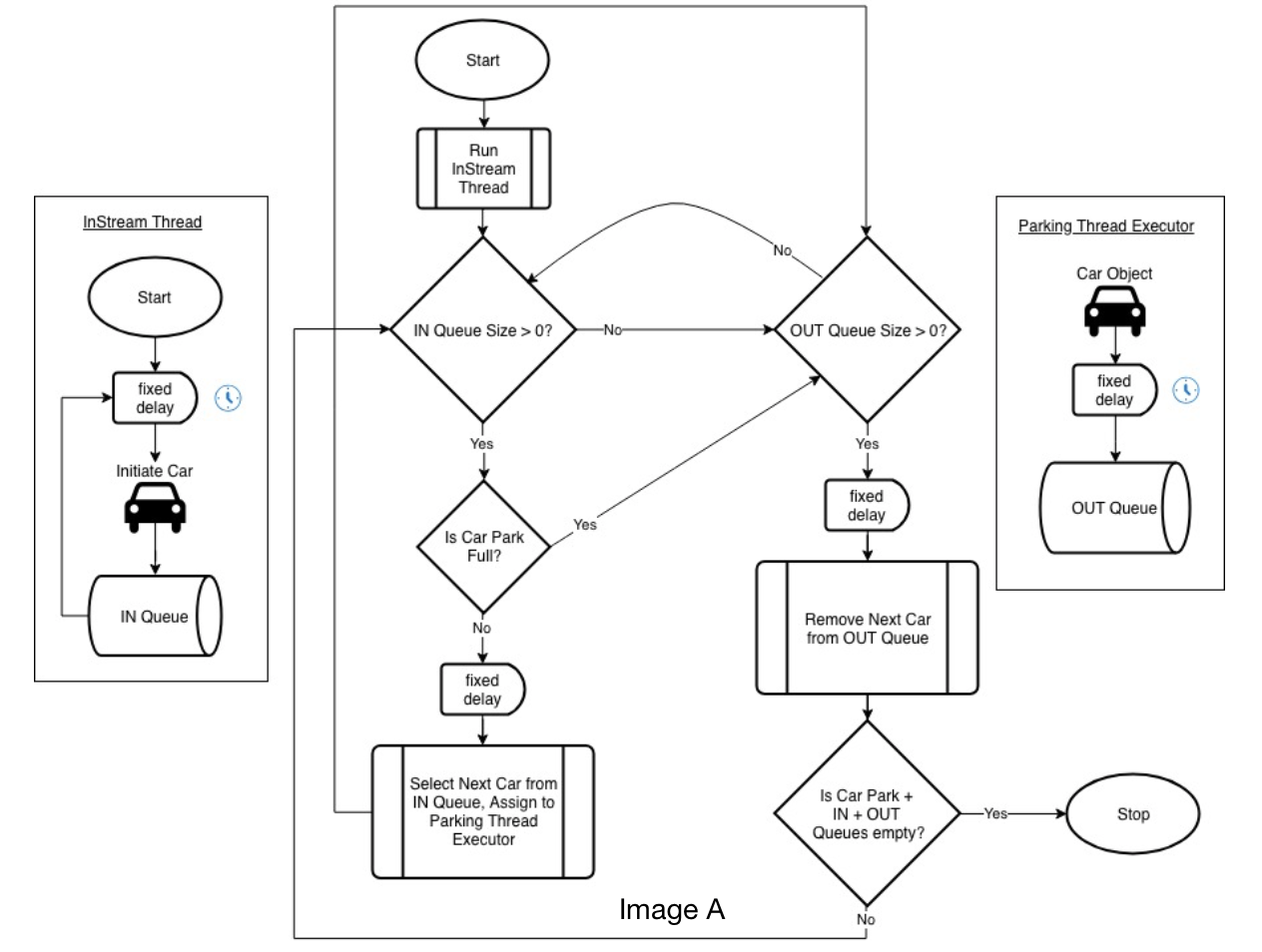
Image A
Testing
|
Test # |
Name |
Objective |
Expected Result |
Actual Result |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Initiate Cars |
Ensure InStream Functionality |
Car objects should populate the IN queue periodically |
As Expected |
|
|
2 |
Liveness |
No infinite waits |
All threads should terminate when their jobs are completed |
As Expected |
This is tested using a limited car scenario to verify executor shutdowns |
|
3 |
Car Park Limit |
The amount of cars allowed in the car park should not exceed the pre-defined space limit |
Once the space limit has been reached, cars in the in queue are no longer accepted until cars have left |
As Expected |
|
Alternative Approach
A 2003 presentation on concurrency describes a different implementation of the car park simulation, which makes use of semaphores as space reservations, and a monitor thread to manage their availability and use per vehicle (Mark Handley, 2003). Using this approach, car arrivals and departures are active thread processes which occur independently, whilst a control monitor manages when arrival and departure can occur through the use of semaphores.
Dining Philosophers
Problem Definition
This problem describes five silent philosophers sat at a round table, each with a fork on either side, as illustrated in image B. Philosophers alter between states of thinking and eating, each for a randomly assigned period of time. The challenge involves the development of a protocol (algorithm) which simulates this situation whilst ensuring none go hungry due to a lack of allocated resources (forks) resulting from deadlock or otherwise.
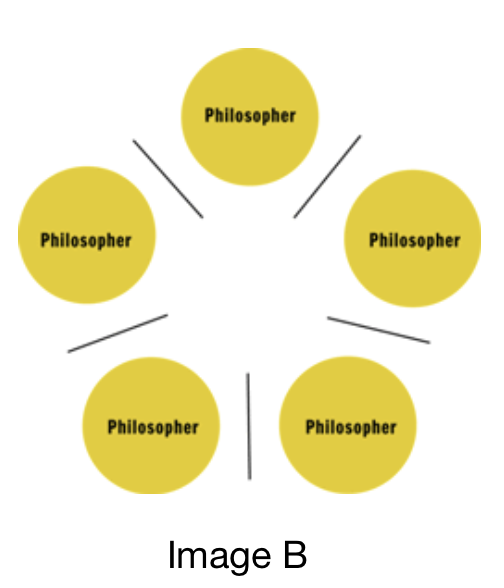
Image B
Solution
Each philosopher is initiated, assigned to a new thread and begins thinking for a random amount of time. When done thinking, the state is updated to hungry and a check is performed to determine if both left and right forks are free. If true, then the philosopher claims both forks by means of a semaphore; a system which keeps track of available and claimed resources. Otherwise, the philosopher waits until the desired forks are returned before being able to claim it. The philosopher then begins eating for a random duration of time before finishing and returning his forks, unsetting the corresponding semaphore. Image C depicts the described process.
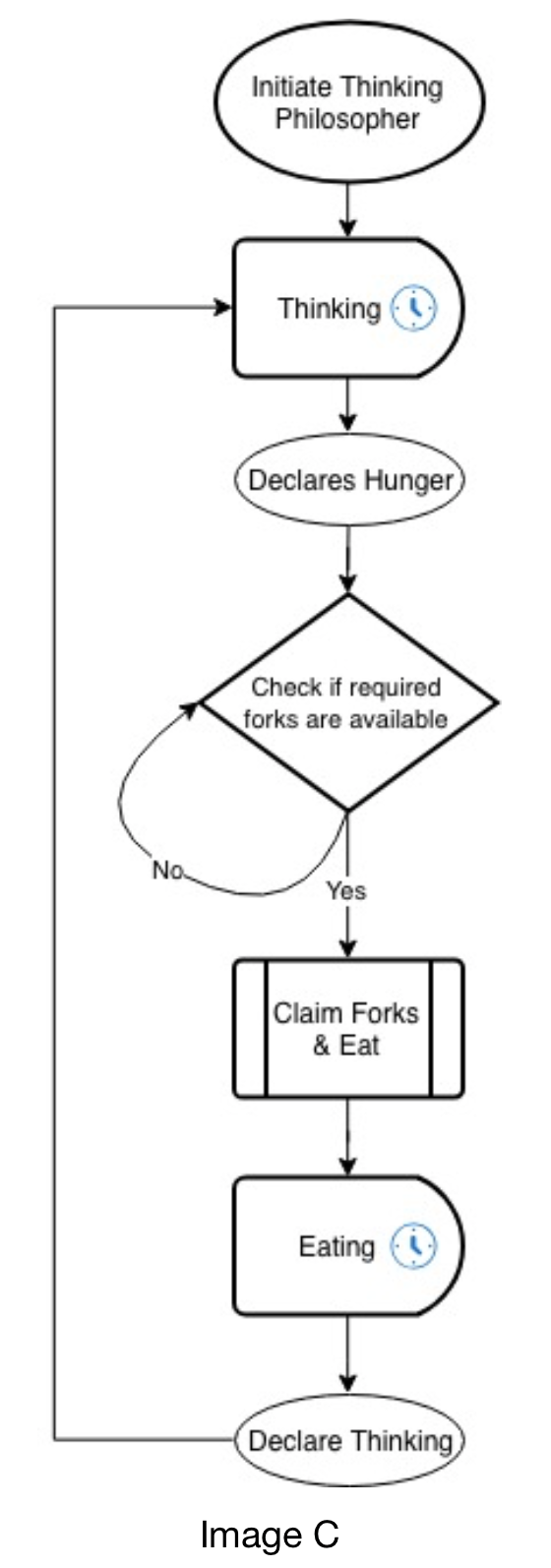
Image C
Logic determining and claiming required forks:
int[] forks = new int[]{0,0,0,0,0}; //SEMAPHORE
private boolean canIeat(){
synchronized(holder.getLock()){ //one claimer at a time
if ((holder.getFork(min(id, (id+1) % 5)) != 1) && (holder.getFork(max(id, (id+1) % 5)) != 1)){ //if both left & right fork is free
holder.setFork((min(id, (id+1) % 5)), 1); //pick up left fork (setting SEMAPHORE)
holder.setFork((max(id, (id+1) % 5)), 1); //pick up right fork (setting SEMAPHORE)
return true; //managed to claim forks
}else{
return false; //no forks available
}
}
}
Where holder.getFork returns a semaphore’s state & holder.setFork claims a semaphore.
In the above snippet, (min/max(id, (id+1) % 5)) is used to select the required semaphores in relation to a specific philosopher, where id represents the philosopher’s unique sequential identifier. The statement selects the forks to the left and right of the philosopher based on the use of min or max respectively. The modulus operator is used to ensure that when the fifth philosopher claims the left fork, the attempt is made on fork one, as opposed to a non-existent index. The entire ‘canIeat’ method is synchronised through a lock object, ensuring only one philosopher can claim forks at any given time.
Testing
|
Test # |
Name |
Objective |
Expected Result |
Actual Result |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Initiate Philosophers |
Ensure Thread Execution |
Each philosopher initiated on separate threads with a unique identifier from 0-4 |
As Expected |
|
|
2 |
Resource Management |
Ensure synchronisation across semaphore claims |
Philosophers claims forks only if they are available and not waiting to be claimed by another thread |
As Expected |
This test ensured desirable functionality of the synchronised lock |
|
3 |
No Starvation |
Ensure deadlock does not occur causing a philosopher to go hungry |
All philosophers have a chance to periodically claim forks and eat |
As Expected |
|
|
4 |
Accurate Referencing |
Ensure philosophers claim the appropriate forks |
Philosophers are only able to claim forks to their left and right |
As Expected |
This test ensured desirable functionality of the modulus operator |
Alternative Approach
A notable improvement to the approach used would involve the implementation of a notification sent to waiting philosopher threads, indicating new forks are available, and hence triggering a check for required forks. This would reduce clock cycles, as threads are being instructed to perform a ‘canIeat’ check as opposed to looping until a true value is returned. Academic papers also describe a solution involving the introduction of a manager, responsible for both queuing hungry philosophers using a first come first serve scheduling system (starvation prevention), and appropriately allocating a token allowing a philosopher to acquire adjacent forks (deadlock prevention) (Deepshikha Bhargava; Sonali Vyas, 2017).
Supermarket Queues
Problem Definition
This simulation requires up to 15 cashiers to process items for customers arriving at random intervals, each with a random number of items. A visual representation should be provided through use of a graphical user interface (GUI). Each cashier should be assigned a fixed standard time to process an item, and each item requires an additional unique processing time. The total processing time for each item is calculated by adding these values. Customers are to select an appropriate queue based on the amount of customers in the queue, and the amount of items per queue. Cashiers are required to automatically close and open queues when a predefined amount of customers has been reached. The customer arrival interval should be user adjustable through the GUI.
Solution
At program startup, queues are created, and cashiers with randomly generated processing times are assigned to each queue. The implemented object oriented solution makes use of a TimerTask to generate new customers. These customers are then processed by an assigner thread, which runs a Queue Control check, randomly assigns items, and selects an appropriate queue for the customer to join based on pre-defined criteria.
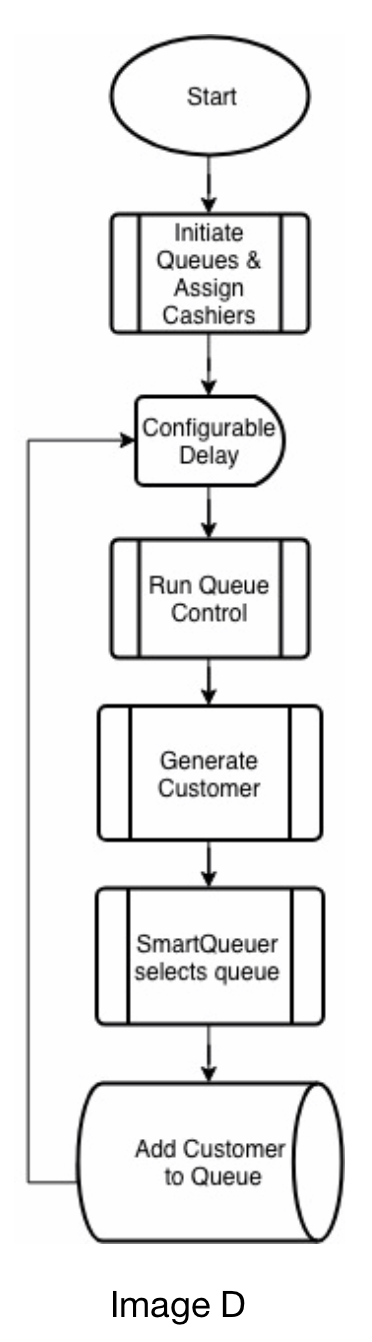
Image D
The Queue Control method handles manual or automatic opening/closing & un/pausing of queues prior to a customer being assigned to one, ensuring pre-defined queue limits and restrictions are observed at all times. This process is depicted using the flowchart provided in Image E. Upon the Queue Control deciding to open a previously closed queue, a Queue Processor thread is initiated. The processor method is responsible for handling sequential customers in a specific queue, taking into account the cashiers fixed processing time, and appending this value to the total item processing time for each customer. A delay is used to simulate the total processing time required for the current customer; upon expiry, the customer is removed from the queue, and the next customer is processed. A visual representation of the processor method is provided in image F.
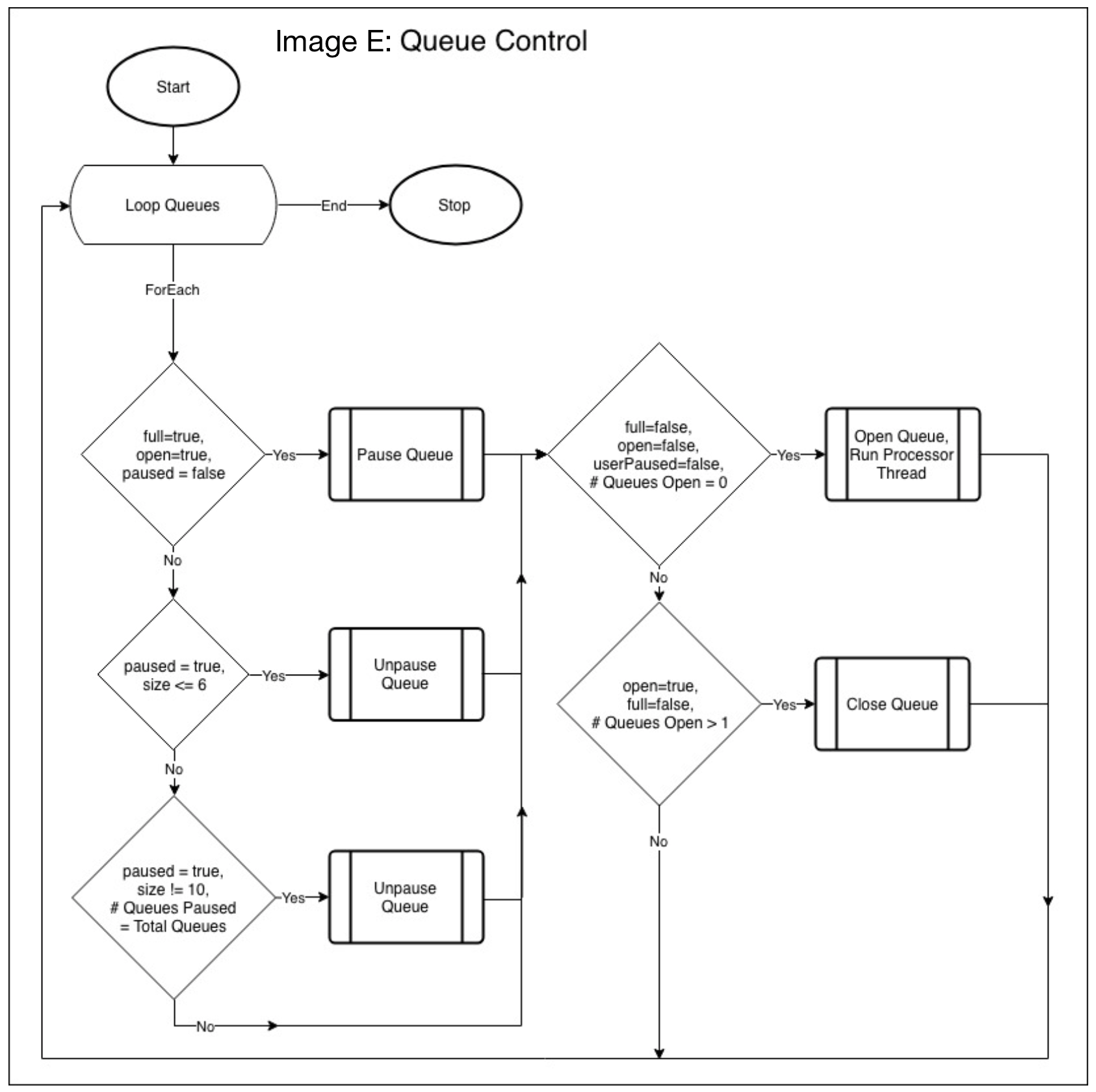
Image E
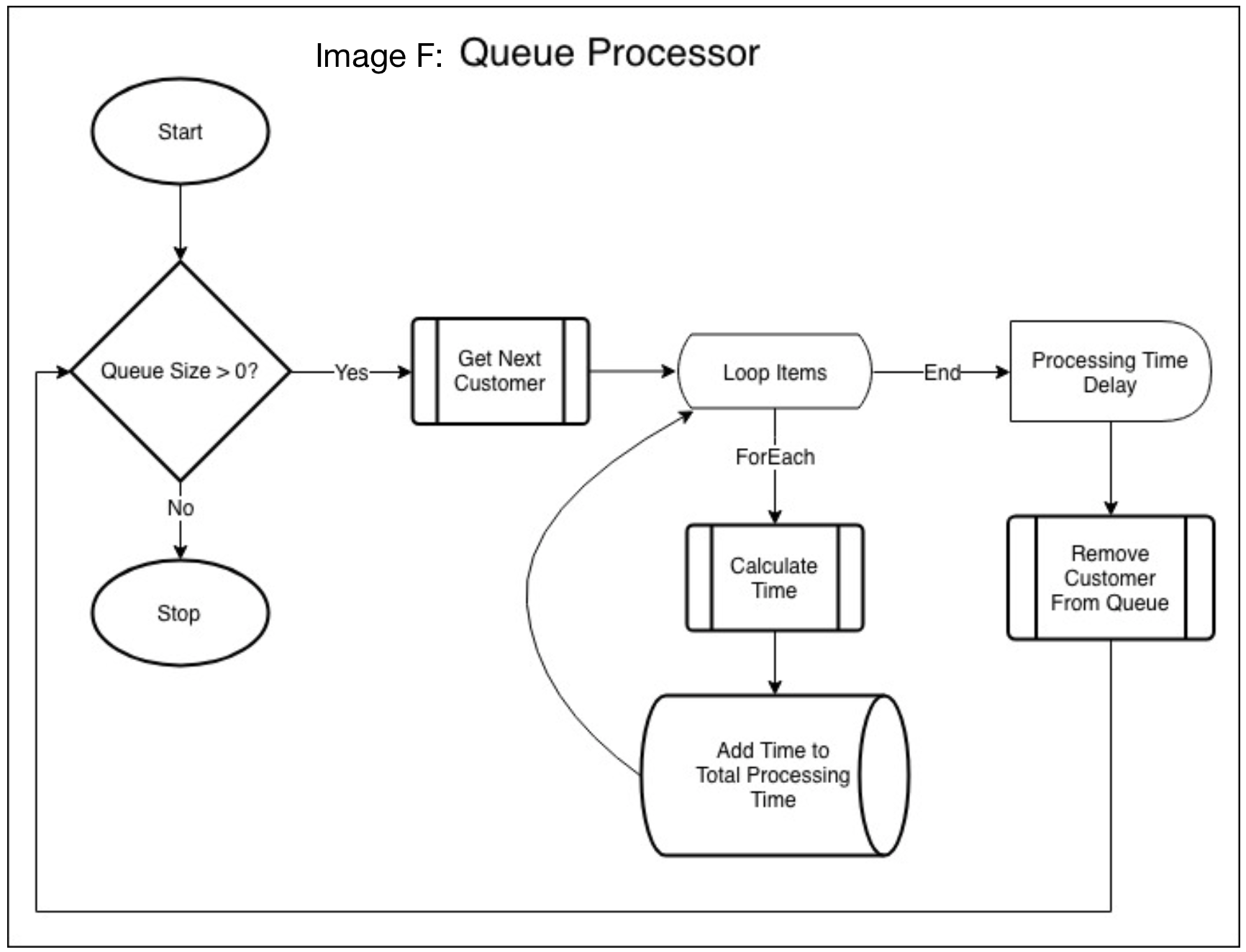
Image F
GUI elements are processed using swing event methods, which are handled on a special thread known as the event dispatch thread. This thread is unique as it allows for swing objects, which are inherently not ‘thread safe’, to be run in multi-threaded environments. Whilst some swing components are documented as thread safe, the majority of swing object methods are not, and therefore risk thread interference or memory consistency errors when invoked from multiple threads (Oracle, 2017). See Image G for GUI.
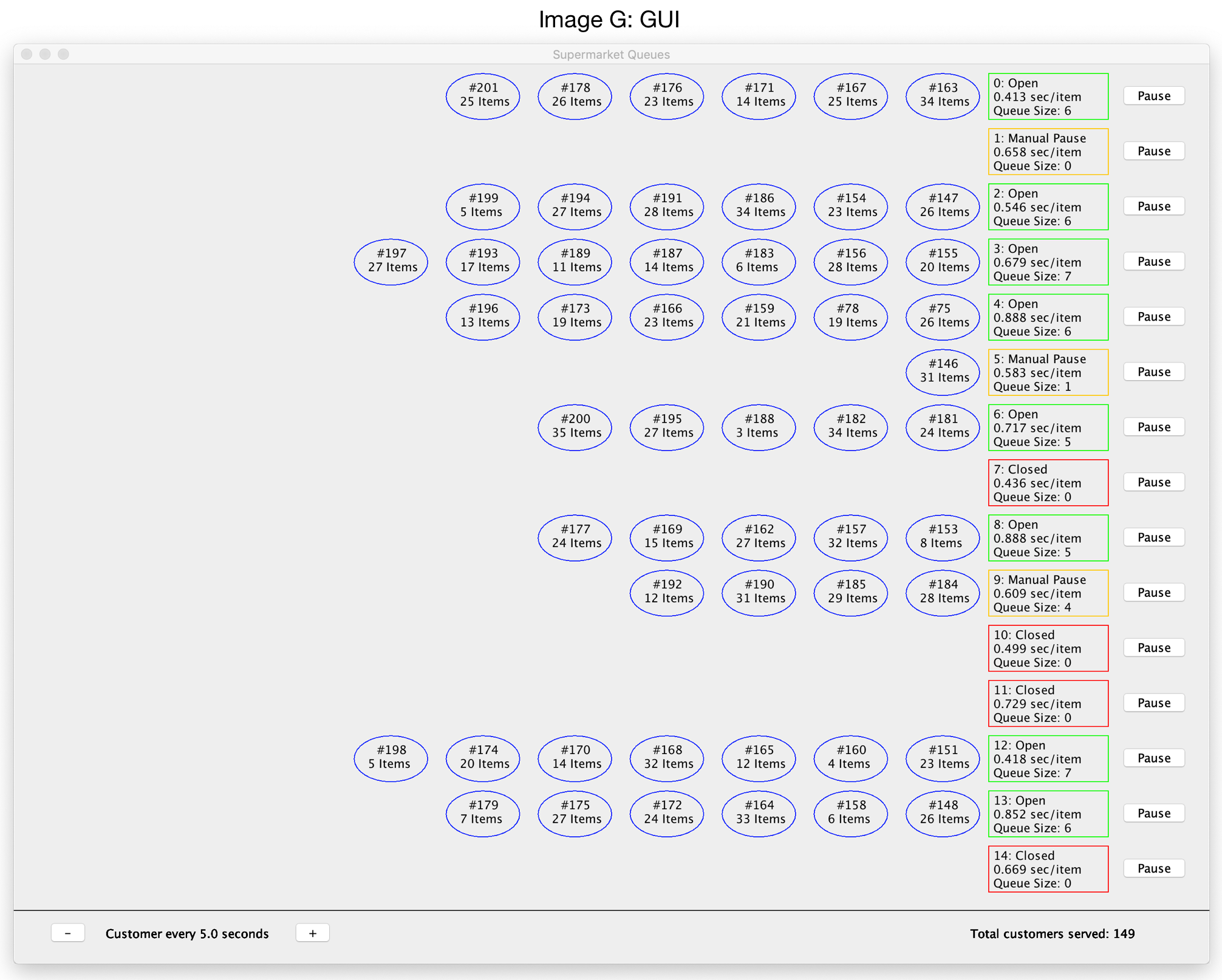
Image G
Testing
|
Test # |
Name |
Objective |
Expected Result |
Actual Result |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Initiate Queues |
Ensure Queues are initiated at program start |
Queues should be initiated and assigned a cashier with a uniquely assigned fixed processing time |
As Expected |
|
|
2 |
Customer Spawning |
Customers should be periodically initiated through TimerTask based on user configurable settings |
Customers should be created at the specified rate of time, and passed onto the Assigner Thread |
As Expected |
|
|
3 |
Assigner Thread |
Assigner calls the Queue Control Check, assigns items to customers, and selects an appropriate queue |
Queue Control Check must complete prior to selecting an appropriate queue. All items should have a unique processing time, and a queue should be selected based on a weighing system, accounting for both the customers in the queue, as well as the total amount of items across all customers. This ensures customer processing times are evenly distributed across queues. |
As Expected |
Queue is chosen based on a calculated weighing of all queues, by multiplying the queue size by the total items across all customers in the queue and selecting the smallest value. |
|
4 |
Queue Control |
Queues are opened/closed & un/paused when preset criteria have been met |
Prior to a customer being assigned to a queue, a check is run to ensure queues are not over capacity, and are re-opened when required. Upon re-opening, start the queue processor |
As Expected |
Queues are looped, and changes to earlier queues are reflected in further queue control processing. |
|
5 |
Queue Processor |
Customers in the queue should be successively processed, simulated using a wait() condition, based on calculated total processing time. |
Total processing time for the next queued customer is calculated based on an aggregate of individual item processing time and the cashier’s fixed processing time. Thread should automatically shutdown when no customers are left |
As Expected |
|
|
6 |
Race Conditions |
Data being created or manipulated completes the operation prior to subsequent read requests to the same piece of data. |
Supermarket queues are initiated before customers are generated and assigned through use of a synchronised lock |
As Expected |
|
Chatroom Server
Problem Definition
This application should allow multiple client connections to a chat server, which broadcasts incoming messages to all other connected users. Clients are identifiable through a username, provided upon connection.
Solution
The chat server is constantly listening for new client connections through a server socket, and opens a new thread for each client. When a new client connects, a socket connection reference is stored in an array list for future communication such as message broadcasting. The management thread stores the userID in main memory, receives & broadcasts incoming messages to all open sockets (connected clients), and manages socket referencing and connections. The first message received from a client will be the identifiable username, and this value is used as a user identifier until the connection is terminated.
Server connection information is pre-defined, and hard coded into the program, thus minimising required user configuration. By default, communication is facilitated using host ‘127.0.0.1’ over port ‘4444’. In the event where a connection to the server cannot be made, the program asks the user to restart the programs, then terminates. Client applications run a broadcast listener thread on program launch, responsible for receiving the socket output stream from the server’s broadcast method, and printing the result to the console.
Testing
|
Test # |
Name |
Objective |
Expected Result |
Actual Result |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Server Socket |
Server is contactable though designated IP address and port |
If server is running on specified IP & port #, program starts normally, otherwise message alerts that server may not be running |
As Expected |
|
|
2 |
Client Connections |
Ensure multiple clients can simultaneously connect & disconnect from the server |
When a new client provides his name, the socket reference is stored and a connection notice is broadcast to all other clients |
As Expected |
Consistent results upon disconnect |
|
3 |
Communication |
Ensure 2-way communication between clients and server |
The client can send the server a message and receive a response |
As Expected |
|
|
4 |
Broadcasting |
All sockets are correctly referenced and stored, and connections are successfully established |
All messages received from the server are sent to all stored socket references, representing connected clients |
As Expected |
|
Guess My Number Game
Problem Definition
This text based game should allow multiple clients to guess a randomly generated number through a socket based server connection. Clients should provide a user id in string format when connecting to the server. The game server should store user performance information, and provide it to the user upon request.
Solution
The choose my number game server is constantly listening for new client connections through a server socket, and opens a new thread for each connected client. This newly created thread is responsible for processing user input and providing desirable feedback; either as a request for a number guess, providing the round outcome (in/correct), and calculating the user’s game statistics.
The client application runs off two thread, one responsible for sending user input to the server through the client’s socket output stream, and the other for receiving a response and displaying it to the user. Server communication configuration is hard-coded into the client application, and facilitated through host ‘127.0.0.1’ over port ‘4444’. When a connection cannot be established, the user is informed that the game server may not be running, and is instructed to restart the application. The first message received from a client will be a username, and this value is used as a user reference for display purposes until the connection is terminated. Subsequent messages are assumed to either be a guessed number, or a request for performance statistics, through the submission of the identifiable command: ‘score’.
Testing
|
Test # |
Name |
Objective |
Expected Result |
Actual Result |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Server Socket |
Server is contactable though designated IP address and port |
If server is running on specified IP & port #, program starts normally, otherwise message alerts that server may not be running |
As Expected |
|
|
2 |
Client Connections |
Ensure multiple clients can simultaneously connect & disconnect from the server |
When a new client provides his name, the socket reference is stored and a connection notice is broadcast to all other clients |
As Expected |
Consistent results upon disconnect |
|
3 |
Communication |
Ensure 2-way communication between clients and server |
The client can send the server a message and receive a response |
As Expected |
|
|
4 |
Game Logic |
The server is able to distinguish between different types of input, and respond accordingly |
Name, score and performance request input values are correctly distinguished, and an appropriate reposes is provided |
As Expected |
Responses include in/correct responses, game stats and invalid input prompt |
|
5 |
Input Data Validity |
Ensure all inputted data is valid, and any exceptions are appropriately dealt with |
Any string other than ‘score’ is to be considered invalid. Any submitted integer which is out of the requested bounds is to be considered invalid. Any value for the username string is considered a valid input. |
As Expected |
The program never crashes on receiving an invalid input, as any exceptions are being caught. The user is always re-asked to guess a number in the same range when an invalid input has been submitted. |
Conclusion
The function and simulation of these programs demonstrate methods for overcoming thread interference, memory consistency, deadlock avoidance, starvation and synchronisation problems that may arise in multi-threaded applications (Rajeev Kumar Singh, 2017). Swing graphical elements have been implemented through an event dispatch thread, allowing for elements which are not inherently thread-thread-safe to be executed in a multi-threaded environment with added features allowing for user interaction. Synchronous Server-Client communication has been facilitated through sockets, allowing for port and ip-based distributed memory program connections over a network. Fully commented java source code for all five programs is provided for reference in the appendix.
References
- Deepshikha Bhargava; Sonali Vyas (2017). Agent based solution for dining philosophers problem. Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8286072 Accessed on December 19th, 2018
- Oracle (2017). The Event Dispatch Thread. Available at: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/uiswing/concurrency/dispatch.html Accessed on December 23rd, 2018
- Mark Handley (2003). 3C03 Concurrency: Semaphores and Monitors. Available at: http://nrg.cs.ucl.ac.uk/mjh/3c03/conc11.pdf Accessed on December 27th, 2018
- Rajeev Kumar Singh (2017). Java Concurrency issues and Thread Synchronization. Available at: https://www.callicoder.com/java-concurrency-issues-and-thread-synchronization/ Accessed on December 27th, 2018
Appendices
Appendix A: Car Park Source Code
Car_Park.java
package car_park;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Car_Park {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InfoHolder holder = new InfoHolder();
ExecutorService managerExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
managerExecutor.submit(new Manager(holder)); //assign car park manager to new thread
managerExecutor.shutdown(); //only called for set number of cars, otherwise runs indefinitely and never shut down
inStream is = new inStream(holder);
is.run(); //start method responsible for initiating new cars in new thread
}
}
class inStream extends Thread{ //Simulate cars arriving at car park
InfoHolder holder;
public inStream(InfoHolder holder){
this.holder = holder;
}
@Override
public void run(){
//for (int i = 0; i < 40; i++){ //set amount of cars (40)
while(true){ //never ending cars
try {
Thread.sleep((int)((Math.random() * (5 - 3)) + 3) * 1000); //car arrives in intervals of between 3 and 5 seconds
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(inStream.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
holder.addtoInQueue(new Car(holder.getNumCars(), holder)); //ARRIVING, add to in queue for manager to process
System.out.println("Car " + holder.getNumCars() + " arrived at IN Queue | Size: " + holder.getInQueueSize()); //alert user
holder.incrementNumCars(); //keep tally of total cars served
//i--; //set amount of cars (40)
}
}
}
InfoHolder.java
package car_park;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class InfoHolder {
private final int spaces = 25;
private int numCars = 0, numCarsInside = 0;
private ArrayList inQueue = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList outQueue = new ArrayList<>();
public synchronized int getSpaces(){
return spaces;
}
public synchronized int getNumCars(){
return numCars;
}
public synchronized void incrementNumCars(){
numCars ++;
}
public synchronized int getNumCarsInside(){
return numCarsInside;
}
public synchronized void incrementNumCarsInside(){
numCarsInside ++;
}
public synchronized void decrementNumCarsInside(){
numCarsInside --;
}
public synchronized void addtoInQueue(Car c){
inQueue.add(c);
}
public synchronized void addtoOutQueue(Car c){
outQueue.add(c);
}
public synchronized Car getNextCarFromInQueue(){
return inQueue.get(0);
}
public synchronized void RemoveNextCarFromInQueue(){
inQueue.remove(0);
}
public synchronized int getInQueueSize() {
return inQueue.size();
}
public synchronized Car getNextCarFromOutQueue(){
return outQueue.get(0);
}
public synchronized void RemoveNextCarFromOutQueue(){
outQueue.remove(0);
}
public synchronized int getOutQueueSize() {
return outQueue.size();
}
}
Manager.java
package car_park;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Manager implements Runnable{
private final long processingTime = 2600; //time required to process a car (processingTime > max car arrival interval/2)
InfoHolder holder;
int i = 0;
ExecutorService carParkingExecutor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); //declare a cached thread pool to assign parked cars to
public Manager(InfoHolder holder){
this.holder = holder;
}
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("Car processed every " + processingTime + " milliseconds");
do{
if (holder.getInQueueSize() > 0){ //run this is cars are present in IN queue
if (holder.getSpaces() > holder.getNumCarsInside()){ //only let a car in if there are available spaces
try {
Thread.sleep(processingTime); //time to process a car
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Manager.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
holder.incrementNumCarsInside(); //keep track of # parked cars
carParkingExecutor.submit(holder.getNextCarFromInQueue()); //select the next car from IN queue and assign it to cached thread pool
System.out.println("Letting IN Car " + holder.getNextCarFromInQueue().getID() + ". Cars inside: " + holder.getNumCarsInside());
holder.RemoveNextCarFromInQueue(); //remove the processed car from IN queue
}
}
if (holder.getOutQueueSize() > 0){ //run this is cars are present in OUT queue
try {
Thread.sleep(processingTime); //time to process a car
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Manager.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
int removedID = holder.getNextCarFromOutQueue().getID(); //for console output reference only
holder.RemoveNextCarFromOutQueue(); //car processed, remove car from OUT queue
holder.decrementNumCarsInside(); //keep track of # parked cars
System.out.println("Letting OUT Car " + removedID + ". Cars inside: " + holder.getNumCarsInside());
if ((holder.getNumCarsInside() + holder.getInQueueSize() + holder.getOutQueueSize() == 0)){ //if no more cars are left inside and none left to process
i = 1; //set i=1, breaking the do/while loop and shutting down the manager.
}
}
}while(i == 0);
//if cars are present in both IN and OUT queue, manager will alternate between queues to process cars, giving equal attention to both regardless of queue size
carParkingExecutor.shutdown(); //only called for set number of cars, otherwise thread pool runs indefinitely
}
}
Car.java
package car_park;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Car implements Runnable {
private final int id;
InfoHolder holder;
public Car(int id, InfoHolder holder){
this.id = id;
this.holder = holder;
}
@Override
public void run(){
int parkFor = (int)((Math.random() * (80 - 15)) + 15) * 1000; //park for a random time between 15 and 80 seconds
System.out.println("Car " + id + " parking for " + parkFor + " milliseconds");
try {
Thread.sleep(parkFor); //PARKED
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Car.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
holder.addtoOutQueue(this); //LEAVING, add to out queue for manager to process
System.out.println("Car " + id + " arrived at OUT Queue | Size: " + holder.getOutQueueSize());
}
public synchronized int getID(){
return id;
}
}
Appendix B: Dining Philosophers Source Code
Dining_Philosophers.java
package dining_philosophers;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Dining_Philosophers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InfoHolder holder = new InfoHolder();
Initiator p = new Initiator(holder);
p.GeneratePhilosophers();
}
}
class Initiator {
InfoHolder holder;
public Initiator(InfoHolder holder){
this.holder = holder;
}
public void GeneratePhilosophers(){
ExecutorService philosopherExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //create new thread pool of 5 for our 5 philosophers
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
philosopherExecutor.submit(new Philosopher(i, holder)); //assign each philosopher to a new thread
System.out.println("Philosopher " + i + ": Thinking"); //user info
}
philosopherExecutor.shutdown(); //wait for tasks to finish then shutdown (tasks are indefinite)
}
}
InfoHolder.java
package dining_philosophers;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class InfoHolder {
private int[] forks = new int[]{0,0,0,0,0}; //SEMAPHORE
private Object lock = new Object();
public synchronized Object getLock(){
return lock;
}
public synchronized int getFork(int i){
return forks[i]; //get semaphore value
}
public synchronized void setFork(int i, int s){
if (s == 0 || s == 1){ //error handling
forks[i] = s; //set semaphore value
}
}
}
Philosopher.java
package dining_philosophers;
import static java.lang.Math.min;
import static java.lang.Math.max;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Philosopher implements Runnable {
private final int id;
private int state = 1; // 1 = thinking (default), 2 = hungry, 3 = eating
private long thinkingTime, eatingTime; //randomly generated
InfoHolder holder;
public Philosopher(int id, InfoHolder holder){
this.id = id;
this.holder = holder;
}
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
//should wait for notification on ready instead of checking every clock cycle
//if thinking
if (state == 1){
thinkingTime = (int)((Math.random() * (12 - 3)) + 3) * 1000; //random assigned thinking time
try {
Thread.sleep(thinkingTime); //THINK
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Philosopher.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
//after thinking, set hungry
System.out.println("Philosopher " + id + ": Hungry & Waiting"); //user info
this.state = 2; //update state
}
//if hungry
if ((state == 2) && (canIeat() == true)){ //if philosopher is hungry and forks are available
//if we managed to claim both forks (once hungry, essentially loops here till both forks available)
//we have both forks; set to eating
System.out.println("Philosopher " + id + ": Eating"); //user info
this.state = 3; //update state
eatingTime = (int)((Math.random() * (8 - 3)) + 3) * 1000; //randomly assigned eating time
try {
Thread.sleep(eatingTime); //EAT
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Philosopher.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
//after eating, set thinking
System.out.println("Philosopher " + id + ": Thinking"); //user info
this.state = 1; //update state
holder.setFork((max(id, (id+1) % 5)), 0); //return right fork (equivalent to UNsetting SEMAPHORE)
holder.setFork((min(id, (id+1) % 5)), 0); //return left fork (equivalent to UNsetting SEMAPHORE)
}
}
}
public synchronized int getState(){
return state;
}
public synchronized int getID(){
return id;
}
private boolean canIeat(){
synchronized(holder.getLock()){ //one claimer at a time. This ensures only one philosopher can check for and pick up forks simultaneously
if ((holder.getFork(min(id, (id+1) % 5)) != 1) && (holder.getFork(max(id, (id+1) % 5)) != 1)){ //if both left & right fork is free
holder.setFork((min(id, (id+1) % 5)), 1); //pick up left fork (equivalent to setting SEMAPHORE)
holder.setFork((max(id, (id+1) % 5)), 1); //pick up right fork (equivalent to setting SEMAPHORE)
return true; //managed to claim forks
}else{
return false; //no forks available
}
}
}
}
Appendix C: Supermarket Queues Source Code
Supermarket_Checkout.java
package supermarket_checkout;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Supermarket_Checkout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InfoHolder holder = new InfoHolder();
Initiator sc = new Initiator(holder);
sc.FreshQueues();
sc.CustomerGenerator();
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable() { //GUI Swing Thread
@Override
public void run() {
new GUI(holder);
}
});
}
}
class Initiator {
InfoHolder holder;
public Initiator(InfoHolder holder){
this.holder = holder;
}
public void FreshQueues(){
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { //define new thread
public void run() {
synchronized(holder.getFqAcLock()) { //synchronise with lock to ensure queues are created prior to customers being assigned
holder.clearQueues(); //clean palette
for (int i = 0; i < holder.getQueueCount(); i++){ //iterate for each queue
Cashier c = new Cashier(i, 0.4, 0.9, holder); //new cashier | id, minSpeed, maxSpeed (per item in seconds)
Queue q = new Queue(i, c, holder); //new queue, containing new cashier
holder.createQueue(q); //add to arraylist for future referencing (shared memory)
}
}
}
});
t1.start(); //start the thread
}
public void CustomerGenerator(){
long customerEvery = (int)(holder.getSecsPerCustomer() * 1000); //value for number of seconds between automatic customer spawn
holder.getCustomerTimer().scheduleAtFixedRate(holder.getNewCustomerTask(), customerEvery, customerEvery); //timer to run AssignCustomer at fixed intervals
System.out.println("Customers Arriving every " + customerEvery + " milliseconds...");//system log
}
}
class AssignCustomer extends TimerTask{
InfoHolder holder;
public AssignCustomer(InfoHolder holder){
this.holder = holder;
}
@Override
public void run(){
synchronized(holder.getFqAcLock()) { //ensure this isnt happening at the same time as queues are being created with a lock synchronisation
ExecutorService assignCustomerExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); //new single thread for the new customer assigner
assignCustomerExecutor.submit(new Assigner(holder.getCustomerCount(), holder)); //pass the assigner to the newly defined thread
assignCustomerExecutor.shutdown(); //shutdown naturally when all tasks within the thread are complete
}
}
}
InfoHolder.java
package supermarket_checkout;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Timer;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class InfoHolder {
private int queueCount = 15, customerCount = 0, customersServed = 0, itemCount = 0, minItems = 3, maxItems = 35;
private double SecsPerCustomer = 3;
private ArrayList queues = new ArrayList<>();
private Object lock = new Object();
private Object fq_ac_lock = new Object();
private Timer customerTimer = new Timer();
AssignCustomer CustomerTask;
public synchronized Object getFqAcLock(){
return fq_ac_lock;
}
public synchronized Object getLock(){
return lock;
}
public synchronized Timer getCustomerTimer(){
return customerTimer;
}
public synchronized AssignCustomer getNewCustomerTask(){
CustomerTask = new AssignCustomer(this);
return CustomerTask;
}
public synchronized void cancelCustomerTask(){
CustomerTask.cancel();
}
public synchronized int getQueueCount(){
return queueCount;
}
public synchronized void setQueueCount(int q){
this.queueCount = q;
}
public synchronized double getSecsPerCustomer(){
return SecsPerCustomer;
}
public synchronized void setSecsPerCustomer(double cps){
this.SecsPerCustomer = cps;
}
public synchronized int getCustomerCount(){
return customerCount;
}
public synchronized void IncrementCustomerCount(){
customerCount ++;
}
public synchronized int getCustomersServed(){
return customersServed;
}
public synchronized void IncrementCustomersServed(){
customersServed ++;
}
public synchronized int getItemCount(){
return itemCount;
}
public synchronized void IncrementItemCount(){
itemCount ++;
}
public synchronized int getMinItems(){
return minItems;
}
public synchronized void setMinItems(int min){
this.minItems = min;
}
public synchronized int getMaxItems(){
return maxItems;
}
public synchronized void setMaxItems(int max){
this.maxItems = max;
}
public synchronized void createQueue(Queue q){
queues.add(q.getID(),q);
}
public synchronized Queue getQueue(int i){
return queues.get(i);
}
public synchronized ArrayList getQueues(){
return queues;
}
public synchronized void setQueue(Queue q){
queues.set(q.getID(),q);
}
public synchronized void clearQueues(){
queues.clear();
}
public synchronized int getQueueSize(int queue){
Queue q = queues.get(queue);
return q.getQueueSize();
}
}
Assigner.java
package supermarket_checkout;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Assigner implements Runnable {
private final int customerID;
InfoHolder holder;
public Assigner(int customerID, InfoHolder holder) {
this.customerID = customerID;
this.holder = holder;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Customer c = new Customer(customerID, holder); //define new customer
holder.IncrementCustomerCount(); //stats update
//assign items to customer
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { //item assigner thread. Generates random amount of items each with random processing time for this customer
public void run() {
Random rand = new Random();
int randomNum = rand.nextInt((holder.getMaxItems() - holder.getMinItems()) + 1) + holder.getMinItems(); //determine number of items to generate
if (randomNum <= 0){//validity check
randomNum = 1;//lil fix
}
for (int j=0; j < randomNum; j++){//for each item to be generated
Item i = new Item(holder.getItemCount(),0.2,0.7);//generate the item, assigning a min&max processing time between 0.2&0.7 seconds
holder.IncrementItemCount();//stats update
c.addItem(i);//add the item to the customer
}
}
});
t1.start(); //start generating the items
queueControl(); //make sure queues are appropriately un/paused & closed/opened
int i = smartQueuer(); //find a queue to put this customer in
try {
t1.join(); //make sure the items have been generated and assigned before proceeding further
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Assigner.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
//add customer to queue
if (i != 16){ //make sure we've found an existing queue
holder.getQueue(i).addCustomer(c); //add the customer
}
}
private int smartQueuer(){
int weight = 0, queueID = 16;
for (Queue aq: holder.getQueues()) { //loop each queue
if (aq.getOpen() == true && aq.getPaused() == false && aq.getOverride() == false){ //if open & not paused
int queueSize = aq.getQueueSize();
if (queueSize == 0){//validity check
queueSize = 1; //lil fix
}
int itemAmmount = 0;
for (Customer customers: aq.getCustomers()) { //cycle all customers in queue
itemAmmount += customers.getItemCount(); //get total items in queue across all customers
}
if (itemAmmount == 0){ //validity check
itemAmmount = 1;//lil fix
}
if (weight == 0){ //for the first queue
weight = (queueSize * itemAmmount); //set the initial value for weight
}
if ((queueSize * itemAmmount) <= weight){ //if the value is greater or equal to a previous queue's highest weight, override the value
weight = (queueSize * itemAmmount); //set new weight high value
queueID = aq.getID(); //remember the queues id for assigning customer
}
}
}
return queueID; //return chosen queue ID value
}
private void queueControl(){
//set global queue stats
int numOpen = 0, numPaused = 0;
for (Queue aq: holder.getQueues()) {
if (aq.getOpen() == true && aq.getPaused() == false && aq.getOverride() == false){
numOpen ++;
}else if (aq.getPaused() == true || aq.getOverride() == true){
numPaused ++;
}
}
for (Queue aq: holder.getQueues()) { //for each queue
//get queue info
boolean open = aq.getOpen();
boolean full = false;
if (aq.getQueueSize() >= 10){
full = true;
}
if (full == true && open == true && aq.getPaused() == false){
aq.setPaused(true); //pause queue
System.out.println("Paused Queue " + aq.getID()); //system log
numOpen --; //update queue stats
numPaused ++;//update queue stats
}else if ((aq.getPaused() == true) && (aq.getQueueSize() <= 6)){
aq.setPaused(false); //resume queue
System.out.println("Unpaused Queue " + aq.getID()); //system log
numOpen ++;//update queue stats
numPaused --;//update queue stats
}else if ((aq.getPaused() == true) && (aq.getQueueSize() != 10) && (numPaused == holder.getQueueCount())){
aq.setPaused(false); //resume queue
System.out.println("Unpaused Queue " + aq.getID()); //system log
numOpen ++;//update queue stats
numPaused --;//update queue stats
}
if (open == false && full == false && aq.getOverride() == false && numOpen == 0){
aq.setOpen(true); //open queue
numOpen ++;//update queue stats
System.out.println("Opened Queue " + aq.getID()); //system log
}else if (open == true && full == false && aq.getQueueSize() == 0 && numOpen > 1){
aq.setOpen(false); //close queue
numOpen --;//update queue stats
System.out.println("Closed Queue " + aq.getID()); //system log
}
}
}
}
Processor.java
package supermarket_checkout;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Processor implements Runnable{
InfoHolder holder;
int qi;
public Processor(int q, InfoHolder holder) {
this.holder = holder;
this.qi = q;
}
@Override
public void run(){
Queue q = holder.getQueue(qi);
Cashier cashier = q.getCashier(); //get the queues cashier
int cashierTime = (int)(cashier.getItemsPerSec()); //and the cashiers processing time
int i = 0;
do{ //do till queue empty and closed
while (q.getQueueSize() > 0){ //do till queue is closed
int itemTime = 0;
Customer c = q.getNextCustomer(); //get next customer
ArrayList items = c.getItems(); //get the customers items
for (Item item: items) { //loop for each item
itemTime += (int)(item.getProcessingTime()); //get the total processing time for all items
}
int totalTime = (cashierTime * c.getItemCount()) + itemTime; //quick maths to incorporate cashier processing time to get total time required
try {
Thread.sleep(totalTime); //sleep for that amount of time to simulate the processing of items
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(Processor.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
System.out.println("Cashier " + cashier.getID() + " processed " + c.getItemCount() + " Items for Customer " + q.getNextCustomer().getID() + " in " + (totalTime) + " millisseconds on queue " + q.getID()); //system log
q.RemoveNextCustomer(); //remove customer from the queue
holder.IncrementCustomersServed(); //stats update
if (q.getOpen() == false){ //if no longer open
i = 1; //exit loop once queue empty
}
}
}while(i == 0); //exit do loop once close is detected
}
}
Queue.java
package supermarket_checkout;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Queue {
public boolean open = false, override = false, paused = false;
private final int id;
Cashier cashier;
private ArrayList customers = new ArrayList<>();
InfoHolder holder;
public Queue(int id, Cashier cashier, InfoHolder holder){
this.id = id;
this.holder = holder;
this.cashier = cashier;
}
public boolean getOpen(){
return open;
}
public void setOpen (boolean o) {
this.open = o;
if (o == true){//if were opening the queue
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//start a new thread executor for queue processor
executor.submit(new Processor(this.id, holder)); //start the processor in new thread
executor.shutdown(); //naturally shutdown when all tasks have completed
}
}
public boolean getOverride(){
return override;
}
public void setOverride (boolean o) {
if (o == false && customers.size() != 10){ //unset pause if size limit isnt exceeded
this.paused = o;
}
this.override = o;
}
public boolean getPaused(){
return paused;
}
public void setPaused (boolean o) {
this.paused = o;
}
public int getID(){
return this.id;
}
public Cashier getCashier(){
return cashier;
}
public void addCustomer(Customer c){
customers.add(c);
System.out.println("Customer " + c.getID() + " (" + c.getItemCount() + " items) arrived at Queue " + id + " (queueSize: " + customers.size() + ") greeted by Cashier " + cashier.getID()); //system log
}
public void removeCustomer(Customer c){
customers.remove(customers.indexOf(c));
}
public Customer getNextCustomer(){
return customers.get(0);
}
public void RemoveNextCustomer(){
synchronized(holder.getLock()) { //synchronise with GUI so we dont call an out of bounds array element when drawing customer ovals
customers.remove(0);
}
}
public ArrayList getCustomers(){
return customers;
}
public Customer getCustomer(int i){
return customers.get(i);
}
public int getQueueSize() {
return customers.size();
}
public boolean getEmpty() {
if (customers.isEmpty()){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
Cashier.java
package supermarket_checkout;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Cashier {
private final int id;
private final double itemsPerSec;
public Cashier(int id, double min, double max, InfoHolder holder){
this.id = id;
if (min < max){ //validity check
this.itemsPerSec = (((Math.random() * (max - min)) + min) * 1000); //set cashier processing time per item between defined range
}else{
this.itemsPerSec = (((Math.random() * (0.9 - 0.4)) + 0.4) * 1000); //lil fix
}
}
public int getID(){
return this.id;
}
public double getItemsPerSec(){
return this.itemsPerSec;
}
}
Customer.java
package supermarket_checkout;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Customer{
private final int id;
private ArrayList itemList = new ArrayList<>();
InfoHolder holder;
public Customer(int id, InfoHolder holder){
this.id = id;
this.holder = holder;
}
public int getID(){
return this.id;
}
public void addItem(Item i){
itemList.add(i);
}
public ArrayList getItems(){
return itemList;
}
public Item getNextItem(){
return itemList.get(0);
}
public int getItemCount(){
return itemList.size();
}
}
Item.java
package supermarket_checkout;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class Item {
private final int id;
private final double processingTime;
public Item(int id, double min, double max){
this.id = id;
if (min < max){ //validity check
this.processingTime = ((Math.random() * (max - min)) + min) * 1000; //set item processing between defined range
}else{
this.processingTime = ((Math.random() * (10 - 1)) + 1) * 1000; //lil fix
}
}
public int getID(){
return this.id;
}
public double getProcessingTime(){
return this.processingTime;
}
}
GUI.java
package supermarket_checkout;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.SwingWorker;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class GUI extends JFrame{
InfoHolder holder;
GUI(InfoHolder holder) {
this.holder = holder;
this.setSize(1300,1000);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setTitle("Supermarket Queues");
this.setResizable(false);
start();
this.setVisible(true);
}
private void start() {
SwingWorker paintQueues = new SwingWorker() {
JButton plusbutton = new JButton("+");
JButton minusbutton = new JButton("-");
JButton zeropausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton onepausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton twopausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton threepausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton fourpausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton fivepausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton sixpausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton sevenpausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton eightpausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton ninepausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton tenpausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton elevenpausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton twelvepausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton thirteenpausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
JButton fourteenpausebtn = new JButton("Pause");
@Override
protected Boolean doInBackground() throws Exception {
minusbutton.setBounds(34, 930, 50, 30);
plusbutton.setBounds(300, 930, 50, 30);
zeropausebtn.setBounds(1200, 20, 80, 30);
onepausebtn.setBounds(1200, 80, 80, 30);
twopausebtn.setBounds(1200, 140, 80, 30);
threepausebtn.setBounds(1200, 200, 80, 30);
fourpausebtn.setBounds(1200, 260, 80, 30);
fivepausebtn.setBounds(1200, 320, 80, 30);
sixpausebtn.setBounds(1200, 380, 80, 30);
sevenpausebtn.setBounds(1200, 440, 80, 30);
eightpausebtn.setBounds(1200, 500, 80, 30);
ninepausebtn.setBounds(1200, 560, 80, 30);
tenpausebtn.setBounds(1200, 620, 80, 30);
elevenpausebtn.setBounds(1200, 680, 80, 30);
twelvepausebtn.setBounds(1200, 740, 80, 30);
thirteenpausebtn.setBounds(1200, 800, 80, 30);
fourteenpausebtn.setBounds(1200, 860, 80, 30);
JPanel queues = new JPanel() {
@Override
public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D) g;
g2d.drawLine(0, 920, 1300, 920);
add(minusbutton);
add(plusbutton);
String status;
Color bg;
for(int i=0; i
if (holder.getQueue(i).getPaused() == true){
status = "Paused";
bg = Color.orange;
}
else if (holder.getQueue(i).getOverride() == true){
status = "Manual Pause";
bg = Color.orange;
}else if (holder.getQueue(i).getOpen() == true){
status = "Open";
bg = Color.green;
}else{
status = "Closed";
bg = Color.red;
}
g2d.setColor(bg);
g2d.drawRect(1060, 10+60*i, 130, 50);
g2d.setColor(Color.black);
g2d.drawString(i + ": " + status, 1065, 25+60*i);
g2d.drawString("0." + (int)holder.getQueue(i).getCashier().getItemsPerSec() + " sec/item", 1065, 40+60*i);
g2d.drawString("Queue Size: " + holder.getQueue(i).getQueueSize(), 1065, 55+60*i);
synchronized(holder.getLock()) {
for (int j=0; j
g2d.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g2d.drawOval(970-100*j, 10+60*i, 80, 50);
g2d.setColor(Color.black);
g2d.drawString("#" + holder.getQueue(i).getCustomer(j).getID(), 995-100*j, 30+60*i);
g2d.drawString("" + holder.getQueue(i).getCustomer(j).getItems().size() + " Items", 985-100*j, 45+60*i);
}
}
g2d.drawString("Customer every " + holder.getSecsPerCustomer() + " seconds", 100, 950);
g2d.drawString("Total customers served: " + holder.getCustomersServed(), 1040, 950);
repaint();
}
add(zeropausebtn);
add(onepausebtn);
add(twopausebtn);
add(threepausebtn);
add(fourpausebtn);
add(fivepausebtn);
add(sixpausebtn);
add(sevenpausebtn);
add(eightpausebtn);
add(ninepausebtn);
add(tenpausebtn);
add(elevenpausebtn);
add(twelvepausebtn);
add(thirteenpausebtn);
add(fourteenpausebtn);
}
};
getContentPane().add(queues);
return true;
}
@Override
protected void done() {
plusbutton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
double cps = holder.getSecsPerCustomer();
if(cps < 10){
cps += 0.50;
Double truncatedDouble=new BigDecimal(cps).setScale(1, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue();
holder.cancelCustomerTask();
holder.setSecsPerCustomer(truncatedDouble);
Initiator sc = new Initiator(holder);
sc.CustomerGenerator();
}
}
});
minusbutton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
double cps = holder.getSecsPerCustomer();
if(cps > 1){
cps -= 0.50;
Double truncatedDouble=new BigDecimal(cps).setScale(1, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP).doubleValue();
holder.cancelCustomerTask();
holder.setSecsPerCustomer(truncatedDouble);
Initiator sc = new Initiator(holder);
sc.CustomerGenerator();
}
}
});
zeropausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(0).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(0).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(0).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
onepausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(1).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(1).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(1).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
twopausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(2).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(2).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(2).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
threepausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(3).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(3).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(3).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
fourpausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(4).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(4).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(4).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
fivepausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(5).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(5).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(5).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
sixpausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(6).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(6).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(6).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
sevenpausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(7).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(7).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(7).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
eightpausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(8).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(8).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(8).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
ninepausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(9).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(9).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(9).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
tenpausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(10).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(10).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(10).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
elevenpausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(11).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(11).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(11).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
twelvepausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(12).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(12).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(12).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
thirteenpausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(13).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(13).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(13).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
fourteenpausebtn.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (holder.getQueue(14).getOverride() == true){
holder.getQueue(14).setOverride(false);
}else{
holder.getQueue(14).setOverride(true);
}
}
});
System.out.println("Queues Painted & Operable");
}
};
paintQueues.execute();
}
}
Appendix D: Chatroom Server & Client Source Code
ChatServer.java
package chatserver;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class ChatServer {
final int portNumber = 4444;
InfoHolder holder;
public ChatServer(InfoHolder holder){
this.holder = holder;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
InfoHolder holder = new InfoHolder();
ChatServer cs = new ChatServer(holder);
cs.runServer();
}
public void runServer() throws IOException{
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(portNumber);//define new server socket to facilitate multiple client connections
System.out.println("Server up and ready for connections on port " + portNumber); //server log
while(true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();//accept new connections to the socket
serverThread st = new serverThread(socket, holder); //assign client to new worker thread
st.start(); //start new worker thread
holder.addClientS(socket); //add socket reference to arraylist for future referencing & communications
//System.out.println("Setting client " + st + "on socket " + socket); //server log
}
}
}
InfoHolder.java
package chatserver;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class InfoHolder {
List clientS = new ArrayList();
public synchronized List getClientS(){
return clientS;
}
public synchronized void removeClientS(Socket socket){
clientS.remove(socket);
}
public synchronized void addClientS(Socket socket){
clientS.add(socket);
}
}
serverThread.java
package chatserver;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class serverThread extends Thread {
Socket socket;
String message = null;
InfoHolder holder;
String userid = "";
public serverThread(Socket socket, InfoHolder holder) {
this.socket = socket;
this.holder = holder;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));//reads client input through socket input stream
boolean name = true; //userid string
while((message = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){ //message = user submitted input
if (name == true){ //for first message
userid = message;
name = false;
System.err.println(userid + " has joined the chatroom! | " + socket); //server log
broadcast(userid + " has joined the chatroom!"); //send to all clients
}else{
System.err.println(userid + ": " + message); //server log
broadcast(userid + ": " + message); //send to all clients
}
}
System.err.println(userid + " has disconnected."); //server log
broadcast(userid + " has disconnected."); //send to all clients
holder.removeClientS(socket); //remove from socket (client) referencing list
socket.close(); //close connection
} catch (IOException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(serverThread.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
public void broadcast(String message) throws IOException {
for(Socket socketS : holder.getClientS()){ //for each client socket
if (socket != socketS){ //except the one that sent the message (this one)
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(socketS.getOutputStream(), true); //facilitates replies to the client vis socket's output stream
printWriter.println(message); //pass the message to output stream
}
}
}
}
ChatClient.java
package chatclient;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class ChatClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
try{
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 4444); //define new socket to facilitate server connections
Thread broadcastListener = new Thread(new Runnable() { //thread to listen for server broadcasted messages
public void run() {
try {
String message = null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); //Reads server reply through socket input stream
while((message = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){ //when message is detected
System.err.println(message); //print the message
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(ChatClient.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
});
broadcastListener.start();//start broadcast listener thread
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));//facilitate reading client input
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);//facilitates communication to the server vis socket's output stream
System.out.println("Whats your name?");
String name = bufferedReader.readLine();//read user input
printWriter.println(name);//send input to the server
System.out.println("Write a message");
while(true){ //loop here
String readerInput = bufferedReader.readLine(); //read user input
if (readerInput != null){ //if input has been given
printWriter.println(readerInput); //send it to the server
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Server is not running at 127.0.0.1 on port 4444. Restart program and try again."); //client error message
//Logger.getLogger(ChatClient.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
}
}
Appendix E: Guess My Number Server & Client Source Code
GuessMyNumber_Server.java
package guessmynumber_server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class GuessMyNumber_Server {
final int portNumber = 4444;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
GuessMyNumber_Server cs = new GuessMyNumber_Server();
cs.runServer();
}
public void runServer() throws IOException{
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(portNumber); //define new server socket to facilitate multiple client connections
System.out.println("Server up and ready for connections on port " + portNumber); //server log
while(true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); //accept new connections to the socket
serverThread st = new serverThread(socket); //assign client to new worker thread
st.start(); //start new worker thread
//System.out.println("Setting client " + st + "on socket " + socket); //server log
}
}
}
serverThread.java
package guessmynumber_server;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class serverThread extends Thread {
Socket socket;
String message = null, randomNumber = null, userid = "";
PrintWriter printWriter;
int attempts = 0, correct = 0, incorrect = 0, uppernum = 10, guessedNum = 0, lowernum = 1;
public serverThread(Socket socket) throws IOException {
this.socket = socket;
printWriter = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true); //facilitates replies to the client vis socket's output stream
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); //reads client input through socket input stream
boolean name = true; //userid string
while((message = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){
if (name == true){ //for first message
userid = message;
name = false;
System.err.println(userid + " wants to Guess My Number! | " + socket); //server console log
reply("Guess My Number from 1 to 10"); //ask user to guess number
BufferedReader guessedNumberInput = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));//reads clients guessed number input through socket input stream
while((message = guessedNumberInput.readLine()) != null){ //if input is given
if(message.equals("score") == true){ //if it equals score, provide game stats
reply("----------------");
reply("UserID: " + userid);
reply("# Attempts: " + attempts);
reply("# Correct: " + correct);
reply("# Incorrect: " + incorrect);
reply("----------------");
}else{ //otherwise
try{ //to ensure integer is provided
int i = (int)((Math.random() * (uppernum - lowernum)) + lowernum); //random number in given range
randomNumber = "" + i;//convert to text for comparison
guessedNum = Integer.parseInt(message);//convert to integer for comparison
if(guessedNum <= uppernum && guessedNum >= lowernum){ //ensure provided guessed number is in range
attempts ++; //stats update
if(message.equals(randomNumber) == true){//guessed number = random number
correct ++;//update stats
System.err.println(userid + " Guessed my Number! (" + i + ")"); //WINNER, server log
reply("Correct! My Number was: " + message); //update the client
}else{
incorrect ++; //update stats
System.err.println(userid + " Couldn't Guess my Number! (Guess: " + message + ", Answer: " + i + ")"); //LOSER, server log
reply("Wrong! My Number was: " + i); //update the client
}
uppernum = (int)((Math.random() * (99 - 10)) + 10);//choose un upper number between 10 & 99
lowernum = uppernum-9; //lower number = upper number-9 for a consistent range
}else{
reply("Invalid Input. Try Again.");//let the user know input is outside range
}
}catch(NumberFormatException e){
reply("Invalid Input. Try Again"); //let the user know input is not an integer
}
}
reply("Guess My Number from " + lowernum + " to " + uppernum); //ask the user to guess a number in random range
}
}
}
System.err.println(userid + " has disconnected.");//server log
socket.close();//close connection
} catch (IOException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(serverThread.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
public void reply(String message) throws IOException {
printWriter.println(message);
}
}
GuessMyNumber_Client.java
package guessmynumber_client;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
*
* @author chrismiceli
*/
public class GuessMyNumber_Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 4444); //define new socket to facilitate server connections
Thread replyListener = new Thread(new Runnable() { //thread to listen for server replies
public void run() {
try {
String message = null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); //Reads server reply through socket input stream
while((message = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null){ //when message is detected
System.err.println(message); //print message
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(GuessMyNumber_Client.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
}
}
});
replyListener.start(); //start reply listener
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));//facilitate reading client input
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true); //facilitates communication to the server vis socket's output stream
System.out.println("Whats your name?");
String name = bufferedReader.readLine(); //read user input
printWriter.println(name); //send to server
System.out.println("Welcome to Guess My Number");
System.out.println("type 'score' for stats");
while(true){ //loop here
String readerInput = bufferedReader.readLine(); //read user input
if (readerInput != null){ //if input has been given
printWriter.println(readerInput);//send input to the server
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Server is not running at 127.0.0.1 on port 4444. Restart program and try again."); //client error message
//Logger.getLogger(ChatClient.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, e);
}
}
}
Ratings